You have to learn some real tricks to get views filtered just the way you want, especially with dates. Dates are fun in that the filter can only compare a date column to an exact date or [Today]. Here's two examples that should get you a start on a wide range of date related filters.
Just Last Month Please
What we need: Only the items where some date is during the last full month. Not 30 days ago, but between the first and last day of last month.
Create two new columns
These two columns calculate the range of dates to show this item. So to figure this out, stop thinking about this month and last month and think about when do you want an item with a certain date displayed. If the item has a date of 2/14/2015 then we want it displayed from 3/1/2015 to 3/31/2015.
For this example the date column we are testing against is named TheDate. (Creative huh!)
Column 1: (to calculate the first day of the month after TheDate)
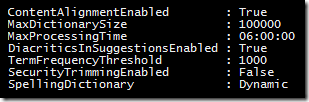
Name: StartDisplayDateForLastMonth
Type: Calculated
Formula: =DATE(YEAR(TheDate),MONTH(TheDate)+1,"1")
The data type returned from this formula is: (o) Date & Time
Date and Time Format: (o) Date Only
Column 2: (to calculate the last day of the month after TheDate)
Name: EndDisplayDateForLastMonth
Type: Calculated
Formula: =DATE(YEAR(TheDate),MONTH(TheDate)+2,0)
The data type returned from this formula is: (o) Date & Time
Date and Time Format: (o) Date Only
Here's a screen shot of the first column. (click to enlarge)

Create the View
Create a view with your usual choice of columns, but not the two we just added. You may want to add these columns for test though.

Display and test the view!
How does it work?
=DATE(YEAR(TheDate),MONTH(TheDate)+1,"1")
DATE needs three values, a year number, a month number and a day number. The first two are easy, if you know a weird fact. YEAR() returns the year number (2015) and MONTH() returns the month number (3). Obviously MONTH()+1 is next month… but what about when it's December plus 1? That's the weird fact. Month 13 bumps up the year value! So DATE(2014,13,5) is 1/5/2015. The 1 at the end of the formula is for day "1" of the month. Don't believe me? Fire up Excel and play around with the DATE function.
=DATE(YEAR(TheDate),MONTH(TheDate)+2,0)
This one depends on another weird fact… day zero is the last day of the previous month! DATE(2015,3,0) is actually 2/28/2015. And of course, DATE(2016,3,0) is 2/29/2016! So what we are doing here is calculating a date 2 months minus one day in the future.
Bonus! What's the date of the 250th day of the year? =DATE(2015,1,250) or 9/7/2015. (I guess that would also be January 250th, 2015!)
What about next month?
Just a slightly different formula.
For the start date: =DATE(YEAR(TheDate),MONTH(TheDate)-1,"1")
For the end date: =DATE(YEAR(TheDate),MONTH(TheDate),0)
What an easy way to create these?
Fire up Excel! (And see this article: http://techtrainingnotes.blogspot.com/2010/08/sharepoint-creating-calculated-column.html)
Have fun!
.