This article applies to SharePoint 2010, 2013 and 2016.
If you have worked around SharePoint for a while then you have heard the phrase "Everything is a list…". If everything is a list then everything should be an "item", right? Turns out that that is almost a fact. With the exception of only a handful of Content Types, they all inherit from"Item". In the end everything inherits from a base type named "System". The listing below is from a 2013 publishing site with a few extra features enabled to find as many Content Types as possible. The 2016 list is very similar, but is missing some of the Business Intelligence content types (Excel Services?).
A few examples:
- Task <- Item <- System
- Document <- Item <- System
- Video <- System Media Collection <- Document Set <- Document Collection Folder <- Folder <- Item <- System
What does not inherit from Item?
- Common Indicator Columns <- System (hidden)
- And the types that inherit from it:
- Excel based Status Indicator <- Common Indicator Columns <- System
- Fixed Value based Status Indicator <- Common Indicator Columns <- System
- SharePoint List based Status Indicator <- Common Indicator Columns <- System
- SQL Server Analysis Services based Status Indicator <- Common Indicator Columns <- System
PowerShell to the rescue… again.
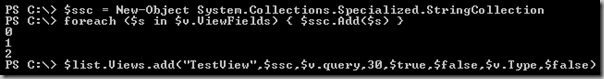
To dump the hierarchy of Content Types I wrote a little PowerShell script that uses a recursive function. Just edit the URL to your site and you can get your list of Content Types.
If you wanted to see the inheritance pattern another way, add the ID of the Content Type to your output, or just do a test like the following and note the pattern in the IDs:
$web.ContentTypes | sort id | Select id, name
The PowerShell script:
function Get-CTypeParent ($ctype, $TTNstr)
{
if ($ctype.name -NE "System") {
$TTNstr = $TTNstr + " <- " + $ctype.parent.name;
$TTNstr = Get-CTypeParent $ctype.parent $TTNstr
}
return $TTNstr;
}
$site = Get-SPSite http://yourserver/sites/yourSite
$web = $site.RootWeb
$web.ContentTypes | sort Group, Name |
group Group |
foreach { $_.Group |
foreach
-Begin {"`n" + $_.Name}
-Process { $str=" " + $_.Name ; Get-CTypeParent $_ $str }
}
The list of Content Types and their family history!
This list is from SharePoint 2013. The 2016 list is very similar, but is missing some of the Business Intelligence content types (Excel Services?).
_Hidden
Administrative Task <- Task <- Item <- System
Approval Workflow Task (en-US) <- SharePoint Server Workflow Task <- Workflow Task <- Task <- Item <- System
Collect Feedback Workflow Task (en-US) <- SharePoint Server Workflow Task <- Workflow Task <- Task <- Item <- System
Collect Signatures Workflow Task (en-US) <- SharePoint Server Workflow Task <- Workflow Task <- Task <- Item <- System
Common Indicator Columns <- System
Design File <- Document <- Item <- System
Device Channel <- Item <- System
Device Channel Mappings <- Document <- Item <- System
Display Template <- Document <- Item <- System
Display Template Code <- Display Template <- Document <- Item <- System
Document Collection Folder <- Folder <- Item <- System
DomainGroup <- Item <- System
Health Analyzer Report <- Item <- System
Health Analyzer Rule Definition <- Item <- System
InfoPath Form Template <- Document <- Item <- System
Office Data Connection File <- Document <- Item <- System
Page Output Cache <- Item <- System
PerformancePoint Base <- Item <- System
PerformancePoint Monitoring Document Type <- Document <- Item <- System
Person <- Item <- System
Project Policy <- Item <- System
Published Link <- Item <- System
Publishing Approval Workflow Task (en-US) <- SharePoint Server Workflow Task <- Workflow Task <- Task <- Item <- System
Reusable HTML <- Item <- System
Reusable Text <- Item <- System
RootOfList <- Folder <- Item <- System
Rule <- Item <- System
SharePoint Server Workflow Task <- Workflow Task <- Task <- Item <- System
SharePointGroup <- Item <- System
Signatures Workflow Task Deprecated <- SharePoint Server Workflow Task <- Workflow Task <- Task <- Item <- System
System
System Master Page <- Document <- Item <- System
System Media Collection <- Document Set <- Document Collection Folder <- Folder <- Item <- System
System Page <- Document <- Item <- System
System Page Layout <- Document <- Item <- System
Translation Package <- Document <- Item <- System
Translation Status <- Document <- Item <- System
Universal Data Connection File <- Document <- Item <- System
User Workflow Document <- Document <- Item <- System
Workflow History <- Item <- System
Workflow Task <- Task <- Item <- System
WorkflowServiceDefinition <- Item <- System
WorkflowServiceSubscription <- Item <- Systemvi
Business Intelligence
Excel based Status Indicator <- Common Indicator Columns <- System
Fixed Value based Status Indicator <- Common Indicator Columns <- System
Report <- Document <- Item <- System
Report Document <- Document <- Item <- System
SharePoint List based Status Indicator <- Common Indicator Columns <- System
SQL Server Analysis Services based Status Indicator <- Common Indicator Columns <- System
Web Part Page with Status List <- Document <- Item <- System
Community Content Types
Category <- Item <- System
Community Member <- Site Membership <- Item <- System
Site Membership <- Item <- System
Digital Asset Content Types
Audio <- Rich Media Asset <- Document <- Item <- System
Image <- Rich Media Asset <- Document <- Item <- System
Rich Media Asset <- Document <- Item <- System
Video <- System Media Collection <- Document Set <- Document Collection Folder <- Folder <- Item <- System
Video Rendition <- Rich Media Asset <- Document <- Item <- System
Display Template Content Types
Control Display Template <- Display Template <- Document <- Item <- System
Filter Display Template <- Display Template <- Document <- Item <- System
Group Display Template <- Display Template <- Document <- Item <- System
Item Display Template <- Display Template <- Document <- Item <- System
JavaScript Display Template <- Document <- Item <- System
Document Content Types
Basic Page <- Document <- Item <- System
Document <- Item <- System
Dublin Core Columns <- Document <- Item <- System
Form <- Document <- Item <- System
Link to a Document <- Document <- Item <- System
List View Style <- Document <- Item <- System
Master Page <- Document <- Item <- System
Master Page Preview <- Document <- Item <- System
Picture <- Document <- Item <- System
Web Part Page <- Basic Page <- Document <- Item <- System
Wiki Page <- Document <- Item <- System
Document Set Content Types
Document Set <- Document Collection Folder <- Folder <- Item <- System
Folder Content Types
Discussion <- Folder <- Item <- System
Folder <- Item <- System
Summary Task <- Folder <- Item <- System
Group Work Content Types
Circulation <- Item <- System
Holiday <- Item <- System
New Word <- Item <- System
Official Notice <- Item <- System
Phone Call Memo <- Item <- System
Resource <- Item <- System
Resource Group <- Item <- System
Timecard <- Item <- System
Users <- Item <- System
What's New Notification <- Item <- System
List Content Types
Announcement <- Item <- System
Comment <- Item <- System
Contact <- Item <- System
East Asia Contact <- Item <- System
Event <- Item <- System
Issue <- Item <- System
Item <- System
Link <- Item <- System
Message <- Item <- System
Post <- Item <- System
Reservations <- Event <- Item <- System
Schedule <- Event <- Item <- System
Schedule and Reservations <- Event <- Item <- System
Task <- Item <- System
Workflow Task (SharePoint 2013) <- Task <- Item <- System
Page Layout Content Types
Article Page <- Page <- System Page <- Document <- Item <- System
Catalog-Item Reuse <- Page <- System Page <- Document <- Item <- System
Enterprise Wiki Page <- Page <- System Page <- Document <- Item <- System
Error Page <- Page <- System Page <- Document <- Item <- System
Project Page <- Enterprise Wiki Page <- Page <- System Page <- Document <- Item <- System
Redirect Page <- Page <- System Page <- Document <- Item <- System
Welcome Page <- Page <- System Page <- Document <- Item <- System
PerformancePoint
PerformancePoint Dashboard <- PerformancePoint Base <- Item <- System
PerformancePoint Data Source <- PerformancePoint Monitoring Document Type <- Document <- Item <- System
PerformancePoint Filter <- PerformancePoint Base <- Item <- System
PerformancePoint Indicator <- PerformancePoint Base <- Item <- System
PerformancePoint KPI <- PerformancePoint Base <- Item <- System
PerformancePoint Report <- PerformancePoint Base <- Item <- System
PerformancePoint Scorecard <- PerformancePoint Base <- Item <- System
Publishing Content Types
ASP NET Master Page <- System Master Page <- Document <- Item <- System
Html Master Page <- ASP NET Master Page <- System Master Page <- Document <- Item <- System
Html Page Layout <- Page Layout <- System Page Layout <- Document <- Item <- System
Page <- System Page <- Document <- Item <- System
Page Layout <- System Page Layout <- Document <- Item <- System
Special Content Types
Unknown Document Type <- Document <- Item <- System
The List Sorted By Ancestor
Change the last line of the script to the following and you can see another pattern in the inheritance.
$web.contenttypes | sort group, name | group group | foreach { $_.Group | foreach -begin {"`n" + $_.Name} -process { $str=" " + $_.name ; Get-CTypeParent $_ $str } }
System -> Item
System -> Item -> Announcement
System -> Item -> Circulation
System -> Item -> Comment
System -> Item -> Contact
System -> Item -> Device Channel
System -> Item -> Document
System -> Item -> DomainGroup
System -> Item -> East Asia Contact
System -> Item -> Event
System -> Item -> Folder
System -> Item -> Health Analyzer Report
System -> Item -> Health Analyzer Rule Definition
System -> Item -> Holiday
System -> Item -> Issue
System -> Item -> Link
System -> Item -> Message
System -> Item -> New Word
System -> Item -> Official Notice
System -> Item -> Page Output Cache
System -> Item -> PerformancePoint Base
System -> Item -> Person
System -> Item -> Phone Call Memo
System -> Item -> Post
System -> Item -> Published Link
System -> Item -> Resource
System -> Item -> Resource Group
System -> Item -> Reusable HTML
System -> Item -> Reusable Text
System -> Item -> Rule
System -> Item -> SharePointGroup
System -> Item -> Task
System -> Item -> Timecard
System -> Item -> Users
System -> Item -> What's New Notification
System -> Item -> Workflow History
System -> Item -> WorkflowServiceDefinition
System -> Item -> WorkflowServiceSubscription
System -> Item -> Document -> Basic Page
System -> Item -> Document -> Design File
System -> Item -> Document -> Device Channel Mappings
System -> Item -> Document -> Display Template
System -> Item -> Document -> Dublin Core Columns
System -> Item -> Document -> Form
System -> Item -> Document -> InfoPath Form Template
System -> Item -> Document -> JavaScript Display Template
System -> Item -> Document -> Link to a Document
System -> Item -> Document -> List View Style
System -> Item -> Document -> Master Page
System -> Item -> Document -> Master Page Preview
System -> Item -> Document -> Office Data Connection File
System -> Item -> Document -> PerformancePoint Monitoring Document Type
System -> Item -> Document -> Picture
System -> Item -> Document -> Report Document
System -> Item -> Document -> Rich Media Asset
System -> Item -> Document -> System Master Page
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page Layout
System -> Item -> Document -> Translation Package
System -> Item -> Document -> Translation Status
System -> Item -> Document -> Universal Data Connection File
System -> Item -> Document -> Unknown Document Type
System -> Item -> Document -> User Workflow Document
System -> Item -> Document -> Wiki Page
System -> Item -> Document -> Basic Page -> Web Part Page
System -> Item -> Document -> Display Template -> Control Display Template
System -> Item -> Document -> Display Template -> Display Template Code
System -> Item -> Document -> Display Template -> Filter Display Template
System -> Item -> Document -> Display Template -> Group Display Template
System -> Item -> Document -> Display Template -> Item Display Template
System -> Item -> Document -> PerformancePoint Monitoring Document Type -> PerformancePoint Data Source
System -> Item -> Document -> Rich Media Asset -> Audio
System -> Item -> Document -> Rich Media Asset -> Image
System -> Item -> Document -> Rich Media Asset -> Video Rendition
System -> Item -> Document -> System Master Page -> ASP NET Master Page
System -> Item -> Document -> System Master Page -> ASP NET Master Page -> Html Master Page
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page -> Page
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page -> Page -> Article Page
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page -> Page -> Catalog-Item Reuse
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page -> Page -> Enterprise Wiki Page
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page -> Page -> Error Page
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page -> Page -> Redirect Page
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page -> Page -> Welcome Page
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page -> Page -> Enterprise Wiki Page -> Project Page
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page Layout -> Page Layout
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page Layout -> Page Layout -> Html Page Layout
System -> Item -> Event -> Reservations
System -> Item -> Event -> Schedule
System -> Item -> Event -> Schedule and Reservations
System -> Item -> Folder -> Discussion
System -> Item -> Folder -> Document Collection Folder
System -> Item -> Folder -> RootOfList
System -> Item -> Folder -> Summary Task
System -> Item -> Folder -> Document Collection Folder -> Document Set
System -> Item -> Folder -> Document Collection Folder -> Document Set -> System Media Collection
System -> Item -> Folder -> Document Collection Folder -> Document Set -> System Media Collection -> Video
System -> Item -> PerformancePoint Base -> PerformancePoint Dashboard
System -> Item -> PerformancePoint Base -> PerformancePoint Filter
System -> Item -> PerformancePoint Base -> PerformancePoint Indicator
System -> Item -> PerformancePoint Base -> PerformancePoint KPI
System -> Item -> PerformancePoint Base -> PerformancePoint Report
System -> Item -> PerformancePoint Base -> PerformancePoint Scorecard
System -> Item -> Task -> Administrative Task
System -> Item -> Task -> Workflow Task
System -> Item -> Task -> Workflow Task (SharePoint 2013)
System -> Item -> Task -> Workflow Task -> PSWApprovalTask
System -> Item -> Task -> Workflow Task -> SharePoint Server Workflow Task
System -> Item -> Task -> Workflow Task -> SharePoint Server Workflow Task -> Approval Workflow Task (en-US)
System -> Item -> Task -> Workflow Task -> SharePoint Server Workflow Task -> Collect Feedback Workflow Task (en-US)
System -> Item -> Task -> Workflow Task -> SharePoint Server Workflow Task -> Collect Signatures Workflow Task (en-US)
System -> Item -> Task -> Workflow Task -> SharePoint Server Workflow Task -> Publishing Approval Workflow Task (en-US)
System -> Item -> Task -> Workflow Task -> SharePoint Server Workflow Task -> Signatures Workflow Task Deprecated
System -> Item
System -> Item -> Announcement
System -> Item -> Circulation
System -> Item -> Comment
System -> Item -> Contact
System -> Item -> Device Channel
System -> Item -> Document
System -> Item -> DomainGroup
System -> Item -> East Asia Contact
System -> Item -> Event
System -> Item -> Folder
System -> Item -> Health Analyzer Report
System -> Item -> Health Analyzer Rule Definition
System -> Item -> Holiday
System -> Item -> Issue
System -> Item -> Link
System -> Item -> Message
System -> Item -> New Word
System -> Item -> Official Notice
System -> Item -> Page Output Cache
System -> Item -> PerformancePoint Base
System -> Item -> Person
System -> Item -> Phone Call Memo
System -> Item -> Post
System -> Item -> Published Link
System -> Item -> Resource
System -> Item -> Resource Group
System -> Item -> Reusable HTML
System -> Item -> Reusable Text
System -> Item -> Rule
System -> Item -> SharePointGroup
System -> Item -> Task
System -> Item -> Timecard
System -> Item -> Users
System -> Item -> What's New Notification
System -> Item -> Workflow History
System -> Item -> WorkflowServiceDefinition
System -> Item -> WorkflowServiceSubscription
System -> Item -> Document -> Basic Page
System -> Item -> Document -> Design File
System -> Item -> Document -> Device Channel Mappings
System -> Item -> Document -> Display Template
System -> Item -> Document -> Dublin Core Columns
System -> Item -> Document -> Form
System -> Item -> Document -> InfoPath Form Template
System -> Item -> Document -> JavaScript Display Template
System -> Item -> Document -> Link to a Document
System -> Item -> Document -> List View Style
System -> Item -> Document -> Master Page
System -> Item -> Document -> Master Page Preview
System -> Item -> Document -> Office Data Connection File
System -> Item -> Document -> PerformancePoint Monitoring Document Type
System -> Item -> Document -> Picture
System -> Item -> Document -> Report Document
System -> Item -> Document -> Rich Media Asset
System -> Item -> Document -> System Master Page
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page Layout
System -> Item -> Document -> Translation Package
System -> Item -> Document -> Translation Status
System -> Item -> Document -> Universal Data Connection File
System -> Item -> Document -> Unknown Document Type
System -> Item -> Document -> User Workflow Document
System -> Item -> Document -> Wiki Page
System -> Item -> Document -> Basic Page -> Web Part Page
System -> Item -> Document -> Display Template -> Control Display Template
System -> Item -> Document -> Display Template -> Display Template Code
System -> Item -> Document -> Display Template -> Filter Display Template
System -> Item -> Document -> Display Template -> Group Display Template
System -> Item -> Document -> Display Template -> Item Display Template
System -> Item -> Document -> PerformancePoint Monitoring Document Type -> PerformancePoint Data Source
System -> Item -> Document -> Rich Media Asset -> Audio
System -> Item -> Document -> Rich Media Asset -> Image
System -> Item -> Document -> Rich Media Asset -> Video Rendition
System -> Item -> Document -> System Master Page -> ASP NET Master Page
System -> Item -> Document -> System Master Page -> ASP NET Master Page -> Html Master Page
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page -> Page
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page -> Page -> Article Page
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page -> Page -> Catalog-Item Reuse
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page -> Page -> Enterprise Wiki Page
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page -> Page -> Error Page
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page -> Page -> Redirect Page
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page -> Page -> Welcome Page
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page -> Page -> Enterprise Wiki Page -> Project Page
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page Layout -> Page Layout
System -> Item -> Document -> System Page Layout -> Page Layout -> Html Page Layout
System -> Item -> Event -> Reservations
System -> Item -> Event -> Schedule
System -> Item -> Event -> Schedule and Reservations
System -> Item -> Folder -> Discussion
System -> Item -> Folder -> Document Collection Folder
System -> Item -> Folder -> RootOfList
System -> Item -> Folder -> Summary Task
System -> Item -> Folder -> Document Collection Folder -> Document Set
System -> Item -> Folder -> Document Collection Folder -> Document Set -> System Media Collection
System -> Item -> Folder -> Document Collection Folder -> Document Set -> System Media Collection -> Video
System -> Item -> PerformancePoint Base -> PerformancePoint Dashboard
System -> Item -> PerformancePoint Base -> PerformancePoint Filter
System -> Item -> PerformancePoint Base -> PerformancePoint Indicator
System -> Item -> PerformancePoint Base -> PerformancePoint KPI
System -> Item -> PerformancePoint Base -> PerformancePoint Report
System -> Item -> PerformancePoint Base -> PerformancePoint Scorecard
System -> Item -> Task -> Administrative Task
System -> Item -> Task -> Workflow Task
System -> Item -> Task -> Workflow Task (SharePoint 2013)
System -> Item -> Task -> Workflow Task -> PSWApprovalTask
System -> Item -> Task -> Workflow Task -> SharePoint Server Workflow Task
System -> Item -> Task -> Workflow Task -> SharePoint Server Workflow Task -> Approval Workflow Task (en-US)
System -> Item -> Task -> Workflow Task -> SharePoint Server Workflow Task -> Collect Feedback Workflow Task (en-US)
System -> Item -> Task -> Workflow Task -> SharePoint Server Workflow Task -> Collect Signatures Workflow Task (en-US)
System -> Item -> Task -> Workflow Task -> SharePoint Server Workflow Task -> Publishing Approval Workflow Task (en-US)
System -> Item -> Task -> Workflow Task -> SharePoint Server Workflow Task -> Signatures Workflow Task Deprecated